
GMP covers all aspects of production; from the starting materials, premises and equipment to the training and personal hygiene of staff. Detailed, written procedures are essential for each process that could affect the quality of the finished product. There must be systems to provide documented proof that correct procedures are consistently followed at each step in the manufacturing process – every time a product is made. WHO has established detailed guidelines for good manufacturing practice. Many countries have formulated their own requirements for GMP based on WHO GMP. Others have harmonized their requirements.
Good quality must be built in during the manufacturing process; it cannot be tested into the product afterwards. GMP prevents errors that cannot be eliminated through quality control of the finished product. Without GMP it is impossible to be sure that every unit of a medicine or medical device is of the same quality as the units of product tested in the laboratory.
Making poor quality products does not save money. In the long run, it is more expensive finding mistakes after they have been made than preventing them in the first place. GMP is designed to ensure that mistakes do not occur. Implementation of GMP is an investment in good quality product. This will improve the health of the individual patient and the community, as well as benefiting the pharmaceutical industry and health professionals. Making and distributing poor quality products leads to loss of credibility for everyone: both public and private health care and the manufacturer.
GMP rules specify relevant requirements on organization and personnel, premises and facilities, equipment, document management, design and development, procurement, production management, quality control, sales and after-sales services, control of nonconforming products, adverse event monitoring, analysis and improvement etc. And the medical device manufactures shall set up and improve the quality management system in accordance with those GMP rules.
1.GMP for medical device Revision History
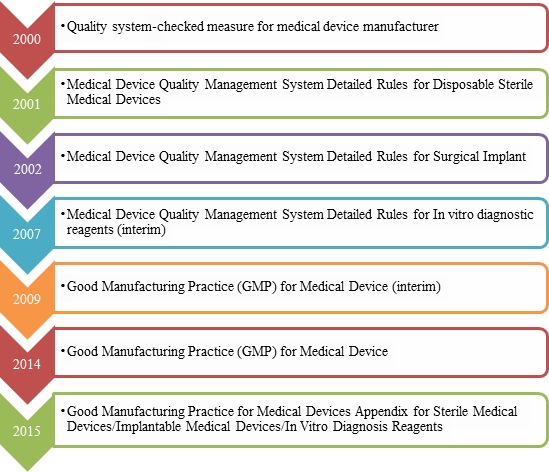
2.The key points of GMP
2.1 Organization & personnel
Note:
Personnel who are engaged in implantable animal medical device and allogeneic medical device shall have trainings in special technology, safeguard and precautious measures according to their product and operation. The personnel include cleaning staff, service staff and so on.
2.2 Premises and facilities
2.3 Equipment
2.4 Document management
2.5 Design and development
If the change of materials, accessories or product function will make an influence on medical device safety and effectiveness, the enterprise shall make a risk evaluation for this change, and shall take measures to reduce the risk to the acceptable levels if necessary, and shall meet the requirements of related regulations for medical device.
2.6 Procurement
Manufacturer shall evaluate and select potential suppliers, contractors, and consultants on the basis of their ability to meet specified requirements, including quality requirements. The evaluation shall be documented.
2.7 Production management
Manufacturer shall compile technological procedure, standard operation procedure, and so on to define the key process and special procedures.
All the information of production shall be traceable.
2.8 Quality control
2.9 Sales and after-sales services
2.10 Control of nonconforming products
2.11 Adverse event monitoring, analysis and improvement
3. Common problems during GMP inspection
- Lack of quality personnel to conduct required material reviews and make disposition decisions;
- Lack of training and evaluation for special positions;
- Environment and facilities noncompliance; grads-design of pressure difference unreasonable;
- Design and development files do not correlate to application dossier for registration;
- Purchasing control confusion, and lack of quality certificate of raw materials;
- Lack of management measures for nonconforming products
